The Pillars of Molecular Oncology Research
Genomic and Proteomic Profiling: The Blueprint of Cancer
At the heart of modern cancer research lies the ability to dissect the genetic and protein landscapes of tumors. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized our understanding by rapidly identifying mutations, gene fusions, and copy number variations that drive cancer. This genomic insight is crucial for precision medicine, allowing for tailored cancer treatment strategies. Beyond DNA, transcriptomics (RNA sequencing) provides a comprehensive view of gene expression patterns, revealing which genes are active or suppressed in cancer cells and identifying novel therapeutic targets. Proteomics, the large-scale study of proteins, complements genomic data by elucidating protein expression, modifications, and interactions. This is vital for discovering new biomarkers for early detection, prognosis, and monitoring treatment response, further advancing the field of molecular biology in oncology.
Cellular and Molecular Biology Techniques: Unraveling Mechanisms
To understand cancer, researchers must study its behavior at the cellular level. Advanced cell culture techniques, including 3D models like organoids and spheroids, provide more physiologically relevant environments than traditional 2D cultures, mimicking the complex tumor microenvironment. These models are invaluable for high-throughput drug discovery and testing. The revolutionary CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology allows for precise manipulation of genes, enabling scientists to validate the functional roles of specific genes in cancer initiation and progression. This powerful tool holds immense promise for developing targeted therapies and even for future gene therapy applications in oncology.
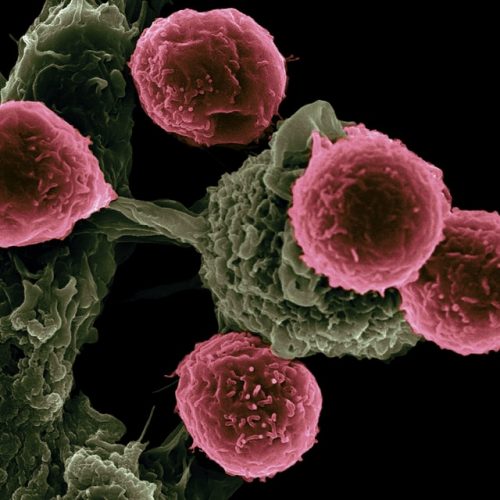
Immunotherapy and Immuno-Oncology Research: Harnessing the Body's Defenses
One of the most significant breakthroughs in recent cancer treatment has been immunotherapy, which harnesses the body's own immune system to fight cancer. Molecular oncology research methods are pivotal in understanding the intricate interactions between tumor cells and the immune system, including mechanisms by which tumors evade immune surveillance. This understanding has led to the development of groundbreaking therapies like CAR T-cell therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ongoing research continues to identify new immune targets and strategies to enhance the efficacy and broaden the applicability of immunotherapy, offering renewed hope for patients with various types of cancer. This area represents a dynamic frontier where biotechnology is rapidly transforming patient outcomes.
Drug Discovery and Development: Targeting Cancer Vulnerabilities
The relentless pursuit of new and more effective anti-cancer agents is a cornerstone of molecular oncology. High-throughput screening methods allow researchers to rapidly test thousands of compounds for their potential to inhibit cancer cell growth or induce cell death. Following initial discovery, promising compounds undergo rigorous preclinical testing in various models, including patient-derived xenografts and organoids, before progressing to human clinical trials. This precision medicine approach, driven by a deep understanding of molecular biology, is transforming drug discovery and shaping the future of cancer treatment.
Stem Cells in Cancer Research: Understanding Origin and Recurrence
A critical area within cancer research focuses on cancer stem cells, a subpopulation of tumor cells believed to possess self-renewal capabilities and the ability to initiate new tumors, drive metastasis, and contribute to therapeutic resistance. Understanding the unique characteristics of these cells is vital for developing therapies that can eradicate the root cause of cancer recurrence. Molecular oncology research methods are employed to identify, isolate, and characterize cancer stem cells, paving the way for novel therapeutic strategies that specifically target these resilient populations, aiming for more durable remissions and preventing disease relapse. This area of study is crucial for improving long-term outcomes in oncology.
Advanced Imaging Techniques: Visualizing the Disease
Beyond molecular and cellular analyses, advanced imaging techniques play a crucial role in both diagnosing and monitoring cancer. Positron Emission Tomography (PET), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and Computed Tomography (CT) provide non-invasive ways to visualize tumors, assess their size, location, and metabolic activity, and track treatment response. At a microscopic level, sophisticated microscopy techniques allow researchers to visualize cellular structures, protein localization, and dynamic processes within cancer cells and their microenvironment, providing invaluable insights into disease progression and therapeutic efficacy. These imaging modalities are integral to comprehensive cancer treatment planning and evaluation.
The journey to conquer cancer is complex, but the relentless pursuit of knowledge through diverse molecular oncology research methods offers immense hope. From understanding the genomic landscape to harnessing the power of the immune system, each method contributes a vital piece to the puzzle. Institutions like Deep Science Workshops and initiatives in Deep Science Implementation are crucial in training the next generation of researchers who will continue to push the boundaries of cancer research, leading to more effective cancer treatment strategies and ultimately, a healthier future. To delve deeper into these critical areas, consider exploring specialized programs that provide comprehensive insights into the molecular basis of cancer therapeutics and targets.